The Teardrop attack is a cyber threat that should not be neglected. It could affect you or your organization and crash your systems. Therefore it is best to understand what a Teardrop attack actually is and how you can protect yourself from it.
Table of Contents
Teardrop attack explained
The Teardrop attack or TCP fragmentation attack is a type of Denial-of-Service attack (DoS attack) that has the main goal to make a network, server, or computer inaccessible by sending them large amounts of altered data packets.
Computer systems that are a bit older have a bug within the code used for handling large amounts of data. That weak spot is the perfect opportunity for initiating the Teardrop attack. Usually, the system should collect all bits and put them in the proper order. Yet, that never happens, and the system continues to wait for pieces that never arrive. As a result, the network, server, or device crashes.
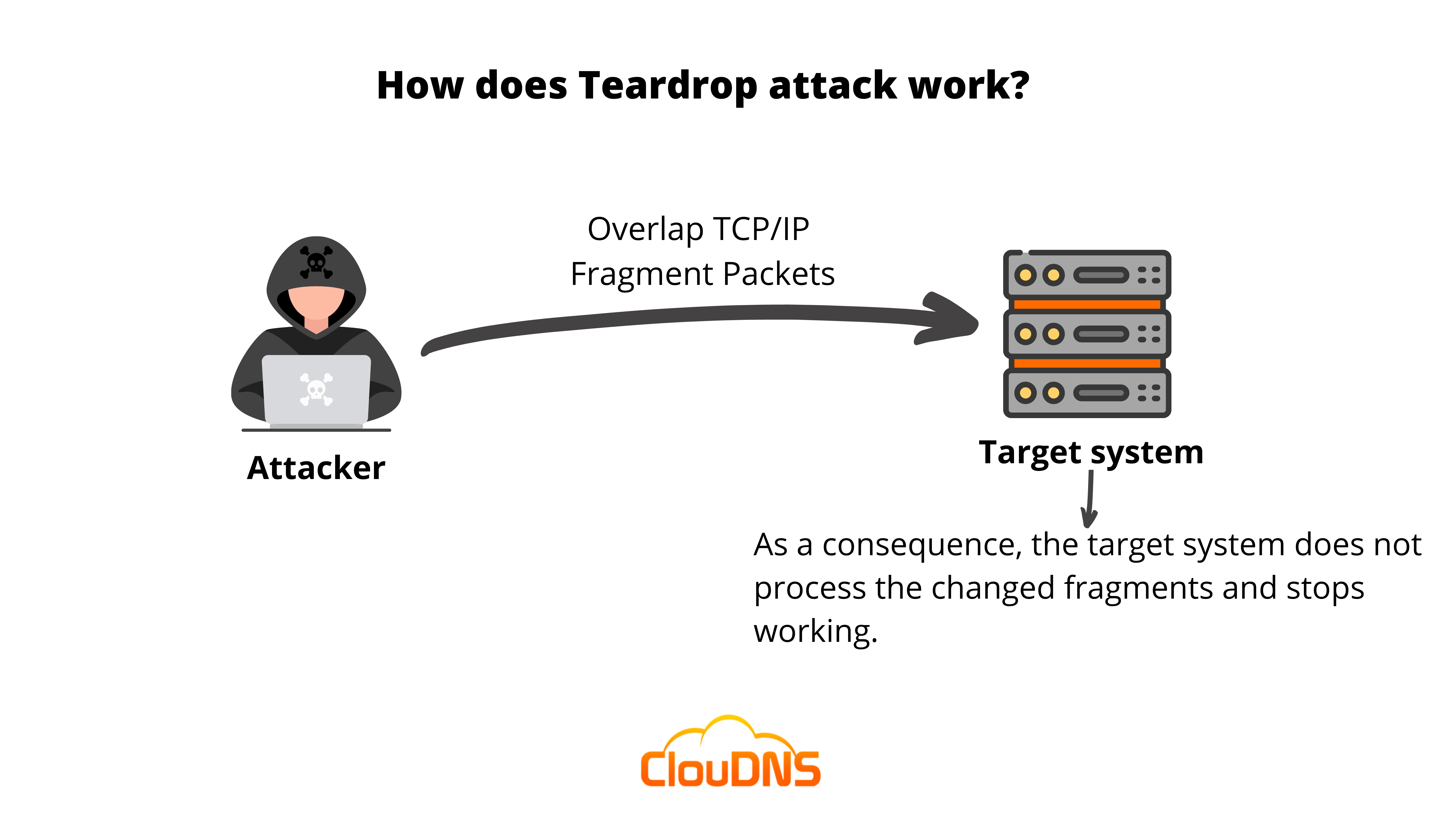
You have probably guessed that the main targets of such DoS attacks are exactly the TCP/IP fragmentation codes. They are performed via a methodology that includes overlapping the fragmented packets of the device, server, or network. When the host tries to reconstruct the packets to their correct order, it typically fails, and eventually, the system crashes permanently. Moreover, the conditions get even worse because of the large amounts of load that are sent to the targeted device. Furthermore, as this malicious threat uses TCP/IP fragments, it’s also a part of the IP fragmentation attack.
The cybercriminals that are completing the attack are more commonly choosing the old versions of operating systems (OS). So, let’s say, for instance, older versions of Windows like Windows NT, Windows 3.1x, Windows 95, Windows 7, Windows Vista. Additionally, other targets could be Linux versions former to 2.0.32 and 2.1.63. Due to their sluggish processing speed and flawed TCP/IP fragments, these systems are unable to aggregate tainted packets.
You are probably assuming that such type of threat is a little bit outdated based on the fact that the new operating systems are not the main targets. However, it would be best if you did not underestimate the potential damage the Teardrop attack could cause. Just think about how many counties, large government, and healthcare organizations are using exactly a lot older versions of operating systems.
Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!
What inspired the name of the attack?
Let’s now look at how it got its name, ‘Teardrop attack.’ The attack’s glitchy code is relatively tiny and fragmented. It is entered slowly and is only a small portion of a large part. This resembles a teardrop in practically every way. It just makes up a small portion of all the tears that a person can shed throughout their lifetime. When it comes to solo, a teardrop won’t have any impact. But when it’s plentiful, it can lead to a breakdown in emotions.
How does it work?
The majority of the systems are created in a simple way that does not allow the transfer of massive amounts of information from a different source in just one attempt. For that reason, systems manage to divide the data into fragments and transfer it like that. Then, relying on the rules established in the software, the recipient reassembles it. For specifying how much information they can process at a time, networks set maximum transmission units (MTUs). In the most common scenarios, a network uses a 1,500-byte limit. However, if you send something more extensive than that, then the following is going to happen:
- Fragmented – The device that wants to send the information, or the router that is related to it, divides the data into pieces – fragment datagrams.
- Sent – Each piece is transferred to the target destination containing headers that have the purpose of defining the precise order for reassembly.
- Reassembled – The server that is set as a target destination remains until the entire collection of fragments arrives. Once each of them is available, the system arranges the information in the proper order and delivers it.
As we mentioned, operating systems (OS) that are a bit aged include a bug. That causes confusion through the phase of reassembly, which makes it possible to use that vulnerability.
Here is how the Teardrop attack is performed, step by step:
- First, the extensive amount of information is divided into small fragments before sending it across the Internet.
- Every piece gets a precise number which defines in which order the fragments should be arranged and assembled to receive the original information.
- The destination server uses the included information in the fragments to organize them in the right sequence.
- In this step, the Teardrop attack interferes and disrupts the fragments’ offset field. That makes it difficult for the device to reassemble the pieces.
- Then a lot of fraudulent packets are delivered on the device or server of the victim. So, finally, that causes the crash of the device.
The good news is that most of the current networks and devices are able to efficiently notice damaged fragmented packets because of their development. If a discrepant packet is recognized, it is possible to restrict it and prevent a Teardrop attack.
What are the effects of the Teardrop DoS attack?
Based on the fact that the Teardrop DoS attack is initiated and targets the TCP/IP reassembly mechanisms and disturbs them from setting together fragmented packets of data. That leads to the overlapping of data packets and overwhelming servers of the victim, which causes them to go down.
Whenever the Teardrop DoS attack is completed, the system, server, or network gets confused. Additionally, it pauses for some time and then crashes. As an effect of it, when the server is down, it is not capable of providing the needed resources, and for instance, your employees won’t be able to do their work at all.
Who are the likely victims of this attack type?
There are some organizations that are more likely to be a target of a Teardrop attack. Typically they are a bit more traditional and are hardly willing to implement the new technologies. It is also common for them to have the understanding that new technologies could affect their operations. Therefore they use a bit older technologies and software. Here are some of the common targets and likely victims of the Teardrop attack:
- Healthcare
More than half of healthcare providers are using some of the old versions of operating systems (OS). In the most popular scenarios, it is exactly Windows 7. That is the reason why they are especially vulnerable to these attacks. Mainly because Microsoft announced that it is not going to continue to support that version of their product.
- Government
Other institutions that are using pretty old systems and technology are precisely the ones related to government. There are cases in which the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) was attacked, and all of the information was not encrypted. Why? Because the system was way too old. Systems like that are very likely to become victims of the Teardrop attack.
- Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI)
In the past years, we have seen a massive improvement and change in the different financial services, and probably all of them implemented the usage of mobile apps. However, if we take a look at what they are implementing to their backend systems, we are going to notice that in most cases, their technologies are not actually brand new. They prefer to operate with legacy systems, but that makes them very vulnerable to Teardrop attacks.
How to protect ourselves?
- Update the version of your OS.
With just this simple task, you are making sure that your device is hard to become a target to such a DoS attack. It is essential not to use an aged OS that is not supported anymore, and there aren’t any security patches. In case you are using such an operating system, you won’t receive updates anymore. That makes you prone to experience not only a Teardrop attack but also some DDoS attack types. (If you are searching for a reliable DNS protection, check our DDoS Protected DNS Service)
- Monitor your systems
You can add an extra layer of security to your system through a Monitoring service. It includes different types of checks. Especially TCP monitoring and Heartbeat мonitoring in a Teardrop attack situation will help a lot. It is a technique for keeping a close eye on a system’s health by regularly sending heartbeat events to a remote monitoring service. For example, if the data included in the heartbeat event does not match the user-defined assertions, it will be notified that something is wrong. So, this would be a clear signal for a defense action.
- Firewall
These attacks target the network layer, so your system should certainly be protected. You can implement a reliable firewall system that filters unwanted data. There are a lot of different types of firewalls. For sure, one of them is going to fit your network’s requirements. It is crucial to enable an efficient filter that is going to help you detect and stop infected data. It serves as an excellent protection method.
How to detect it?
Detecting the presence of a Teardrop Attack can be challenging, considering its ability to camouflage within the network’s regular traffic. However, there are several signs and symptoms that administrators and security personnel can observe:
- System Instability: One of the primary indicators of a Teardrop Attack is the sudden instability or unresponsiveness of systems and network devices. Sluggish response times, increased latency, and interrupted connectivity can indicate that your system is under attack. Users might experience frequent crashes, freezes, or abnormal behavior in applications and services.
- Unusual Network Activity: Strange network behavior, such as an unexpected surge in network traffic or a sudden increase in packet fragmentation, could be a red flag indicating a potential Teardrop Attack. Monitoring network traffic for irregular patterns becomes crucial in detecting such anomalies.
- System Logs and Error Messages: Regularly reviewing system logs and error messages can reveal clues about attempted attacks or system anomalies caused by a Teardrop Attack. Unusual error messages related to packet handling or IP reassembly could hint at malicious activities.
Why are Teardrop attacks so important?
A great number of people are still using systems that are considered very old. Additionally, the companies that provided these tools are not supporting them anymore. For instance, there are still organizations that hold a device that operates with Windows XP. Yet, the support ended back in 2014. There are various cyber threats, and the Teardrop attack is one of them that proves how important it is to update your systems.
In case you are using software that is modern and you update it on time, it is going to be a lot harder for an attacker to initiate a Teardrop attack towards you or your business. The reason for that is simple. The vulnerability that is required for performing the attack just doesn’t exist, and attackers can’t take advantage of it. Therefore it is essential to know the way IP fragmentation attacks such as Teardrop are made.
Real-World Examples of Teardrop Attacks
The Teardrop attack gained popularity in the late 1990s and early 2000s when it targeted legacy systems with vulnerabilities in handling fragmented packets. One of the most significant instances occurred with older versions of Microsoft Windows, particularly Windows NT and Windows 95. These systems had known issues with the TCP/IP reassembly process, which attackers exploited to cause widespread crashes.
In 1997, a series of Teardrop attacks highlighted the severity of this vulnerability. Organizations that relied heavily on Windows-based systems reported frequent system freezes and network failures. These incidents forced Microsoft to release emergency patches to address the issue.
Another example involves older Linux kernels, particularly versions prior to 2.0.32 and 2.1.63, which were also found to be vulnerable. Attackers targeted these systems in Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) campaigns, taking down networks and interrupting critical services.
Although such attacks are less common today due to modern OS updates, legacy systems in industries like healthcare and government still face risks.
Differences Between Teardrop Attacks and Other DoS Attacks
Teardrop attack is a distinct type of denial-of-service (DoS) attack that stands apart from the more common methods, such as SYN floods or UDP floods. Traditional DoS attacks rely on overwhelming a system with a massive volume of traffic, pushing its resources, like bandwidth, CPU, or memory, to their limits and causing it to crash or become unresponsive.
Teardrop attacks, however, take a more targeted approach. They exploit a specific flaw in the way older operating systems handle TCP/IP packet reassembly. By sending fragmented packets with overlapping data, the attack confuses the system during the reassembly process, leading to instability or crashes. Unlike other DoS attacks, this method doesn’t require high traffic volumes to achieve its goal.
Another key difference is the type of systems these attacks target. While volume-based DoS attacks can disrupt almost any system if the traffic is heavy enough, Teardrop attacks are most effective against outdated operating systems with known vulnerabilities in their packet reassembly mechanism. Modern systems with up-to-date software and patches are generally immune to such attacks.
Conclusion
So, now you understand actually how dangerous a Teardrop attack is. It could affect your device, network or computer. For that reason, it is extremely important to keep yourself and your network safe and take the required actions to prevent it.