DNS filtering helps organizations keep networks and users safe by blocking access to malicious and harmful websites. It also allows organizations to customize access policies, accelerate user browsing speeds, and ensure their networks meet IT compliance requirements. Learn more about how DNS filtering works, its benefits, and how it differs from web filtering in this blog post.
Table of Contents
DNS explanation
To understand clearly how DNS filtering operates, we need to explain the purpose of the Domain Name System briefly.
DNS, which stands for “Domain Name System,” converts the names of websites into IP addresses that browsers can recognize. As a result, whenever you visit a website, your browser requests a particular kind of DNS server. This server returns a corresponding IP address after examining the requested domain name. Then, the page can be loaded from there in a split second, providing you full access.
What is DNS filtering?
DNS filtering, or DNS blocking, is a security technique that prevents access to malicious, untrustworthy, or otherwise undesirable domains or IP addresses. When a user attempts to access a web address, the DNS query is compared to a blocklist of undesirable domains or IP addresses. And if a match is found, the domain is not resolved, and access is denied.
How does it work?
It works in a simple way. All DNS queries are routed through a Recursive DNS server (DNS resolver). DNS resolvers that have been specially configured can also act as filters by refusing to resolve queries for specific domains that are tracked in a blocklist, preventing users from accessing those domains. DNS filtering services can also employ an allowlist rather than a blocklist
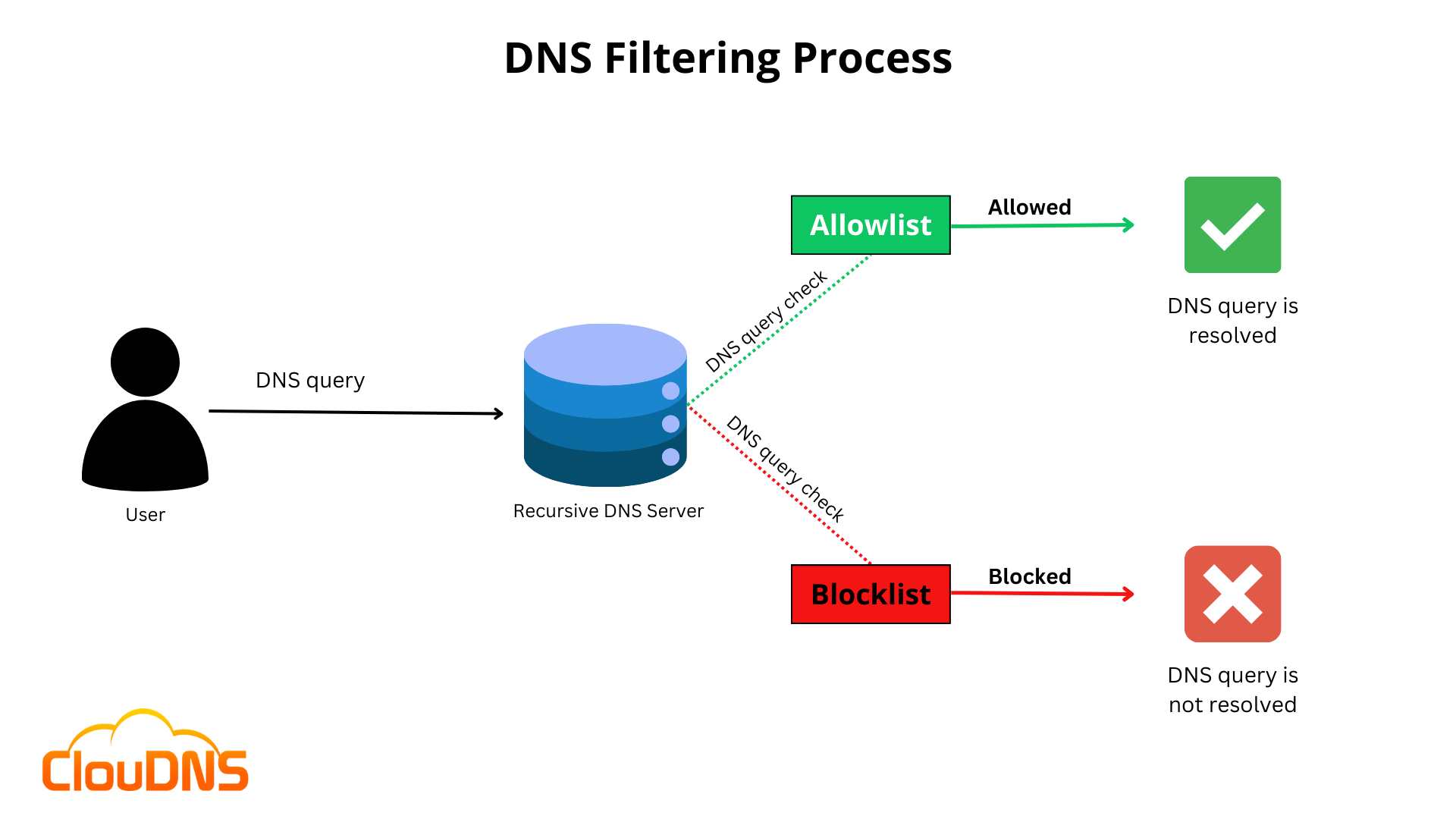
Let’s say an employee for the organization receives a phishing email. It falls for the trick of clicking a link that takes them to malisiousexample.com. The company’s DNS resolving service, which uses DNS filtering, receives a query from the employee’s computer before it loads the webpage. The DNS resolver will reject the request if the malicious website is listed on the company’s blocklist. This will stop maliciousexample.com from loading and stop the phishing attack.
DNS filtering can ban websites either by IP address or domain name:
- By IP address: The DNS resolver tries to resolve every domain, but the resolver won’t send the result back if the querying device’s IP address is on the blocklist.
- By domain: For some domains, the DNS resolver does not even attempt to resolve, or look up, the IP addresses.
What does having a secure DNS server mean?
A secure DNS server is a DNS resolver that filters unsafe or restricted webpages as part of a DNS filtering service. Some secure DNS servers also offer enhanced privacy to protect user data, such as Private DNS servers, which delete all DNS query records after some time.
Since DNS was not intended with security in mind from the start, there are additional techniques to make the DNS process safer besides DNS filtering. For example, the DNSSEC ensures that DNS resolvers provide accurate information and are not compromised. In addition, DNS over TLS (DoT) and DNS over HTTPS (DoH) encrypt DNS queries and responses, making it difficult for attackers to track a user’s DNS requests.
Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!
Why should you filter DNS?
Due to its adaptability, DNS filtering provides customers with advanced customization options. You can select which content types are allowed and which should be blocked based on the requirements of your organization. In addition, you protect your users from harmful content by implementing DNS-based web blocking. In addition, DNS filtering provides additional benefits, such as:
- Stops visitors from visiting dangerous or harmful websites.
- Includes simple category-based filtering, blacklisting and whitelisting.
- It prevents visitors from going to phishing websites.
- Stops the download of potentially illegal files.
- Make browsing safe and secure for network users, Wi-Fi users, and visitors.
- Restricts malware downloads for users
What types of DNS attacks can target me if I don’t have DNS filtering?
- DNS cache poisoning (DNS spoofing): The goal of this attack is to taint the recursive servers, specifically the cached replies. If they are successful, any following query will receive a poisoned response.
- DNS hijacking: This attack aims to send DNS messages to a different domain name server with completely bogus information to redirect users to dangerous web pages. Because it is sent to a different location, malware on the target client PC might enable all DNS requests to be routed to the attacker’s controllable DNS server.
- DNS tunneling: It drills into DNS messaging and passes malware using SSH, TCP, or HTTP. DNS tunneling entails encoding communications in DNS queries and responses. This DNS attack leaks sensitive information, in which case the constantly changing domain names make it very challenging to catch.
DNS filtering vs Web filtering
There are two different kinds of content filtering: DNS filtering and web filtering. DNS filtering restricts website access based on DNS queries. On the other hand, web filtering prevents access to specific websites based on their URL. As DNS filtering can prevent access to websites even before they are loaded, it is often more effective than web filtering.
In general, web filters are less precise than DNS filters. This is because DNS queries are frequently more accurate than URLs. For instance, a DNS query for “example.com” will always result in the same IP address. But, depending on your region, the example.com URL can change. Whether you are logged in, or not can also affect how it changes.
Web filtering typically takes longer than DNS filtering. This is because DNS queries often resolve more quickly than URLs. DNS filtering might also obstruct access to websites using secure connections (HTTPS).
Comparison DNS filtering with other security measures
DNS filtering is a vital security layer, but it’s important to understand how it compares with other measures:
- Firewalls: Firewalls control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. While DNS filter blocks access to harmful domains, firewalls regulate data packets based on source, destination, and types of traffic, offering a different layer of security.
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus programs detect, prevent, and remove malware. DNS filter complements this by preventing access to malicious sites where malware can be downloaded, thus reducing the antivirus software’s load.
- Email Filtering: This specifically targets email threats like phishing and spam. DNS filtering adds an extra layer of security by blocking access to malicious links that might be missed by email filters.
- Endpoint Protection: Endpoint protection focuses on securing endpoints in a network. While this is crucial for detecting and responding to attacks, Domain Name System filtering prevents threats at the network level before they reach endpoints.
Can DNS filtering be bypassed?
While DNS filtering is a powerful way of safeguarding against online threats, it is not infallible. Skilled individuals can bypass DNS filters using various methods such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), proxy servers, or by changing the DNS settings on their devices. These methods allow users to avoid the restrictions set by DNS filtering by routing their internet traffic through different servers. To counteract this, it’s important for organizations to employ a comprehensive security strategy that includes regular updates and additional protective measures alongside DNS filtering, DDoS Protection, DNSSEC, Private DNS servers, etc. These approaches ensure a robust defence against evolving cyber threats, maintaining the integrity of network security.
DNS Filtering in different environments: Home vs. Enterprise
DNS filtering serves distinct roles in home and enterprise settings:
- Home Environment: Primarily used for parental controls and basic security, DNS filtering in homes blocks inappropriate content and protects against common threats. Solutions are typically user-friendly and require minimal configuration.
- Enterprise Environment: In businesses, DNS filtering is a critical component of a multi-layered security strategy. It enforces compliance, safeguards against sophisticated cyber threats, and manages bandwidth usage. Enterprise solutions offer advanced features like detailed reporting, integration with other security systems, and granular policy controls.
Conclusion
DNS filtering is essential for organizations that want to keep their networks and users safe, whether working in a public Wi-Fi environment or within their corporate network. It provides granular customization options to tailor user access policies, block unwanted content, and enhance privacy. With the constant threat of DNS-based attacks on the rise, implementing a reliable DNS filtering service is the key to ensuring a secure connection for all users.