In today’s digital age, the internet has become an integral part of our daily lives, enabling us to connect, shop, and conduct business with ease. However, with these conveniences come new security risks, and one of the most prevalent and dangerous threats is phishing attacks. Phishing attacks are a type of cybercrime that aims to steal sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial details, and personal data, by tricking individuals into revealing it unwittingly. In this blog post, we will delve into what a phishing attack is, how it works, different types of phishing attacks, trends in phishing attacks, and most importantly, how you can protect yourself against them.
Table of Contents
What is a Phishing attack?
A phishing attack is a malicious attempt by cybercriminals to deceive individuals into providing sensitive information through fraudulent emails, messages, or websites. The attackers disguise themselves as trustworthy entities, such as banks, social media platforms, or government agencies, to gain victims’ trust and exploit their vulnerability for personal gain.
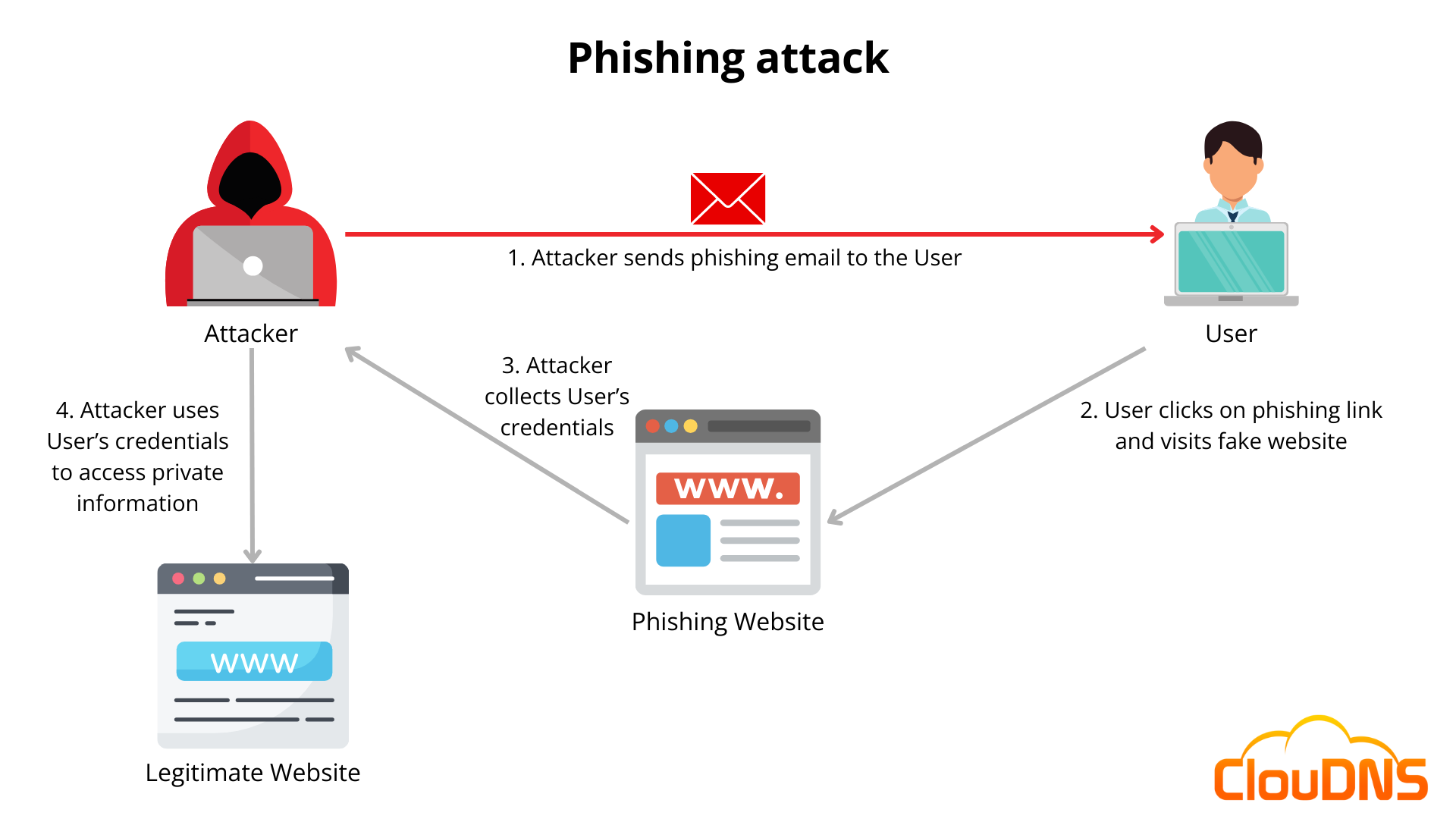
How does it work? Step by step
Here’s how a typical phishing attack unfolds:
- Bait Creation: The first step in a phishing attack involves creating an enticing bait, such as an urgent request to update account information, a tempting offer, or a warning about a compromised account.
- Delivery: The bait is then delivered through various means, such as email, SMS, social media messages, or even malicious ads.
- Deception: The message typically contains a sense of urgency or fear, compelling the recipient to take immediate action without questioning its legitimacy.
- Linking to fake websites: Phishing emails often include links to fake websites that closely resemble legitimate ones. These fake sites are designed to collect the victim’s login credentials and personal information when entered.
- Data collection: Once the victim enters their information, the cybercriminals capture it and can use it for identity theft, financial fraud, or other malicious purposes.
Types of phishing attacks
There are several variations of phishing attacks, including:
- Email phishing: The most common type, where fraudulent emails are sent to deceive recipients into revealing sensitive information.
- Spear phishing: Highly targeted attacks aimed at specific individuals or organizations, often using personalized information to appear more convincing.
- Whaling attacks: Similar to spear phishing but focused on high-profile individuals or executives within an organization.
- Clone phishing: Attackers create a replica of a legitimate email and modify it to include malicious content or links.
- Pharming: Redirects victims to fraudulent websites even if they enter the correct web address.
How do spear phishing attacks differ from standard phishing attacks?
Standard phishing attacks cast a wide net, sending mass emails or messages impersonating well-known entities to deceive as many victims as possible. These attacks use generic content and fake websites to trick recipients into revealing personal information.
In contrast, spear phishing attacks are highly targeted and personalized. Cybercriminals gather specific details about their victims, crafting convincing messages that appear to come from trusted sources like colleagues or business partners. This tailored approach increases the likelihood of success, as victims are more likely to fall for the authenticity of the communication, leading to the disclosure of sensitive data or malware installation.
Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!
2023 Phishing attack Statistics
According to a staggering statistic from IT Governance, an estimated 3.4 billion malevolent emails, mainly in the form of phishing, hit our inboxes every single day, marking it as the predominant form of cybercrime (IT Governance, 2023). The objective? To ensnare unsuspecting individuals into revealing their login credentials. IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report further sheds light on this issue by revealing that stolen credentials, indeed, represent the primary cause of data breaches, accounting for 19% of all cyber attacks (IT Governance, 2023).
The threat intensifies when we shift our gaze towards corporate security. A report by Digital Guardian has identified that a staggering 90% of corporate security breaches can be traced back to phishing attacks (IT Governance, 2023). The toll on organizations is heavy. Each piece of personal information pilfered via a phishing attack, according to Venari Security, translates to an approximate loss of $181. (IT Governance, 2023).
Source: 51 Must Know Phishing Statistics for 2023, IT Governance
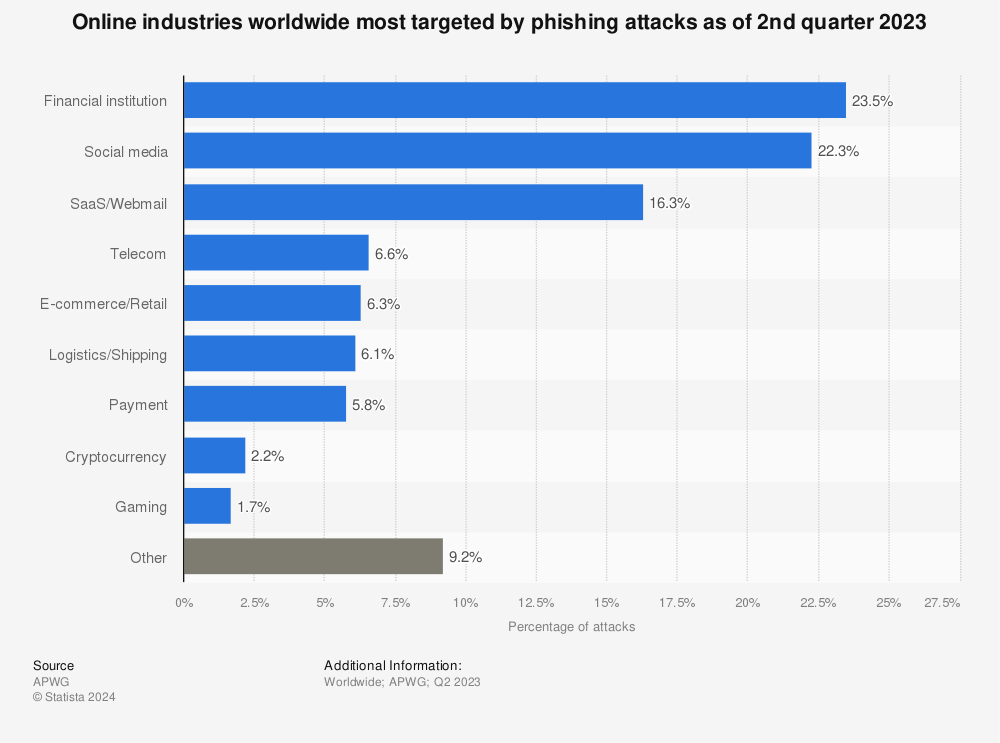
Source: Most Affected Industries by Phishing, Statista
In the ever-evolving landscape of phishing attacks, certain industries tend to be more targeted than others. Statista, a leading provider of market and consumer data, provides an illuminating infographic that delineates the sectors most affected by phishing.
Leading the pack, unsurprisingly, is the financial industry with 23% of phishing attempts directed towards it. This is due to the sensitive and valuable information that this sector holds, making it an attractive target for cybercriminals.
Next up, the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and webmail industries face their fair share of threats with 17% of the phishing attacks aimed at them. This might be attributed to the fact that many SaaS companies hold vast amounts of data on behalf of their clients, making them a rich source for phishing attempts.
Social media platforms are the third most targeted, suffering from 11% of these malicious attempts. The extensive personal and business data that users tend to share on these platforms make them a fertile ground for cybercriminals.
Logistics and shipping sectors, along with e-commerce and retail, each receive 6% and 4% of the phishing attempts respectively. The payment sector is also targeted by 4% of phishing attacks. These industries, dealing with sensitive transactional data, are enticing for hackers who want to exploit the financial and personal information.
The telecom sector, with a share of 3%, and the burgeoning cryptocurrency industry, receiving 2% of phishing attempts, round out the list. It is worth noting that as the popularity of cryptocurrencies continues to grow, they may become an even more lucrative target for phishing in the future.
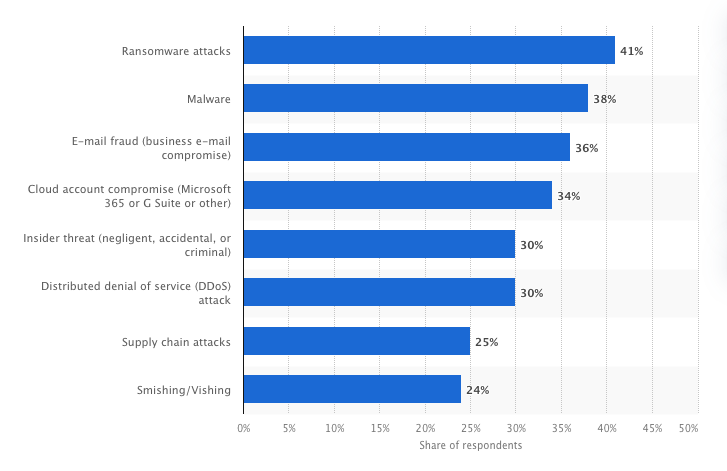
Most significant cybersecurity threats in organizations worldwide (2024)
Phishing attacks play a pivotal role in many of the most significant cybersecurity threats facing organizations today. According to a 2024 survey of Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs), phishing often serves as the gateway that enables attackers to execute broader cybercrimes. Here’s how phishing connects to these top concerns:
- Ransomware Attacks: The leading threat, cited by 41% of CISOs, often begins with phishing emails. These emails lure users into downloading malicious attachments or clicking on links that activate ransomware, encrypting critical data and demanding payment.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): A key concern for 36% of CISOs, BEC scams rely heavily on phishing to impersonate trusted contacts, tricking employees into transferring funds or sharing confidential information.
- Cloud Account Compromise: Highlighted by 34%, phishing attacks frequently target login credentials for cloud platforms like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace, granting attackers unauthorized access to sensitive organizational data.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: Cited by 30%, phishing campaigns can be used to distribute malicious links or attachments that facilitate DDoS attacks, overwhelming organizational systems and causing severe service disruptions.
- Smishing/Vishing: Identified by 24%, these advanced forms of phishing exploit SMS (smishing) or voice calls (vishing) to deceive victims, making them more personal and challenging to detect.
Source: Most significant cybersecurity threats in organizations worldwide, Statista
These findings emphasize that phishing is not just a standalone issue – it is a foundational threat that amplifies the risk of larger, more complex cyberattacks. By addressing phishing vulnerabilities, organizations can mitigate their exposure to these interconnected threats and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture.
Impacts of Phishing Attacks
The consequences of falling victim to a phishing attack can be severe and extensive. For individuals, the theft of personal information can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and damage to personal reputation. In the context of organizations, phishing attacks can result in data breaches, financial fraud, disruption of operations, and loss of customer trust.
Beyond immediate financial and reputational harm, phishing attacks can also be used to launch more advanced cyber threats, such as ransomware, malware infections, and business email compromise (BEC) scams. By compromising the credentials of unsuspecting users, attackers gain access to organizations, enabling them to launch more sophisticated and targeted attacks.
Moreover, the indirect costs associated with phishing attacks, including incident response, remediation efforts, and regulatory fines, can be significant burdens on organizations of all sizes. The reputational damage from a successful phishing attack can ruin an organization’s brand and lose customer trust, potentially leading to long-term business consequences.
How to protect against Phishing Attack?
There are several proactive steps you can take to protect yourself against phishing attacks:
- Anti-phishing software: This type of software can identify phishing content and alert users about potential threats.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This adds an extra layer of security by requiring two types of identification before granting access.
- Monitoring service: With Monitoring service you can keep an eye on your personal data online and alert you if they detect unusual activity.
- DNS records: You can implement SPF, DMARC, DKIM, and PTR records. These email authentication methods help protect against email spoofing and increase email security.
- rDNS: Reverse DNS lookup can verify whether the server is associated with the domain it claims to represent.
- HTTPS and SSL certificates: Look for ‘https‘ in the URL and the padlock symbol in the browser for an SSL certificate that can help to identify secure websites. Phishing websites often lack these security measures, providing users with visual cues of a potential threat.
- Education and awareness: Regular training on phishing attack recognition and safe online habits can be crucial for both businesses and individuals.
- Regular software updates: Keeping your software and systems updated ensures you have the latest security patches, making it harder for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities.
Famous Phishing Attacks
Here are some of the most popular examples of Phishing attacks:
- Target Corporation (2013)
In late 2013, Target, one of the largest retail chains in the United States, fell victim to a sophisticated phishing attack that led to massive consequences. The attack began with a phishing email sent to an HVAC vendor that had access to Target’s network. The attackers then used the compromised vendor credentials to gain entry into Target’s systems. Ultimately, the breach resulted in the theft of over 40 million credit card numbers and personal information of 70 million customers. The incident highlighted the potential cascading impact of phishing attacks on large organizations.
- Sony Pictures (2014)
In 2014, Sony Pictures Entertainment became the target of a highly publicized cyber attack. While the attack included elements beyond phishing, it was initiated through a carefully prepared email. The attackers sent phishing emails to Sony employees, tricking them into revealing login credentials. Afterwards, the attackers unleashed malware that disabled Sony’s computer systems, leading to the exposure of sensitive internal documents, emails, and unreleased films. The incident highlighted the potential for phishing to be a precursor to more extensive and damaging cyber intrusions.
- Facebook and Google (2017)
In 2017, a Lithuanian hacker produced a phishing attack targeting tech giants Facebook and Google. The attacker posed as a legitimate vendor and successfully convinced employees at both companies to wire over $100 million in payments for supposed goods and services. The scam involved fake invoices and email correspondence that appeared to be from reputable suppliers. The incident highlighted the vulnerabilities in the supply chain and payment processes of large corporations, emphasizing the need for strict verification procedures.
Conclusion
The landscape of cybercrime, particularly phishing, is ever-evolving. Therefore, staying informed and proactive in adopting protective measures is crucial. With the knowledge of how phishing works, what the current trends are, and how to defend against these attacks, individuals and organizations can greatly enhance their cybersecurity stance.