Slowloris attack is famous for slowly draining the life out of a website until it can no longer function properly. In addition, this type of attack is known for its ability to cause significant damage to websites and servers, leading to slowdowns, crashes, and data loss. But don’t let that scare you! By understanding how Slowloris attacks work and how to protect your website from them, you can keep your online presence secure and running smoothly. So without any further ado, let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What is the Slowloris attack?
Slowloris attack is a type of Denial of Service (DoS) that aims to flood a targeted server with incomplete HTTP requests. As a result, it overwhelms the target with a slow and steady stream of traffic. The attack works by sending a massive amount of incomplete HTTP requests, exploiting the server’s limited number of connections and eventually leading to a complete shutdown.
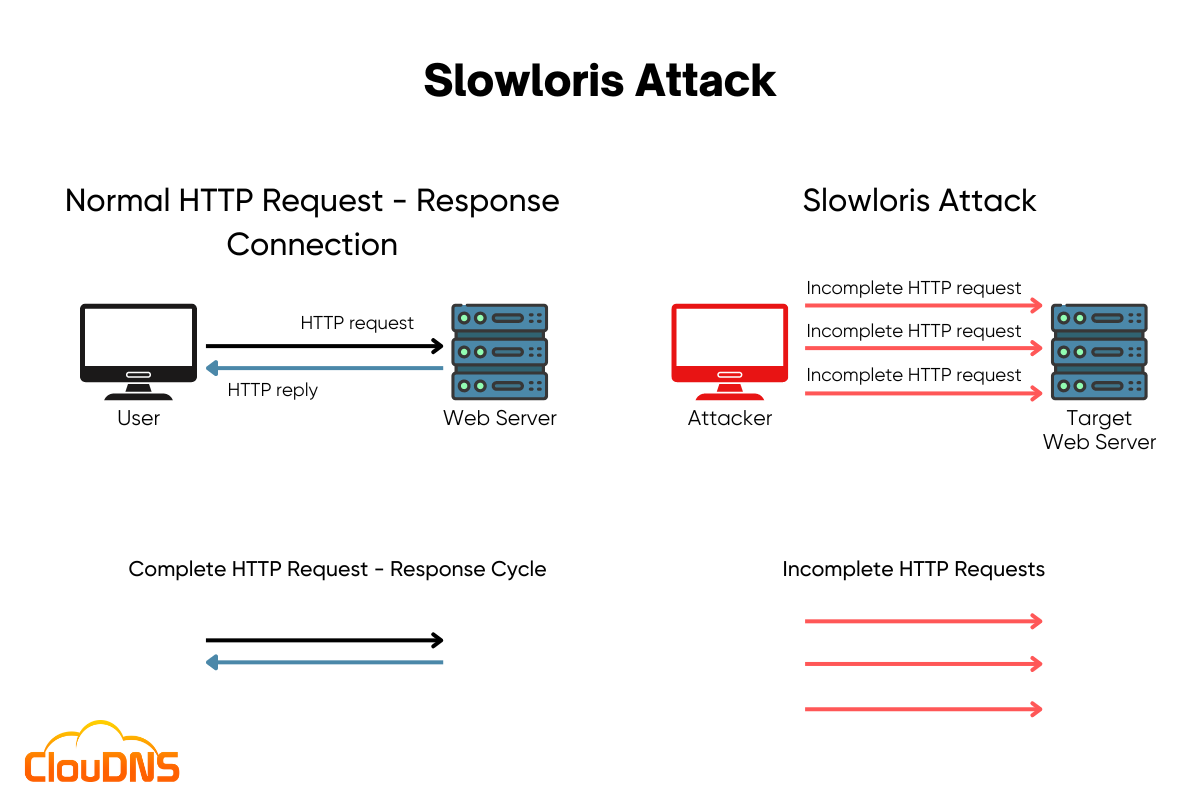
The key characteristic of the Slowloris attack is that it utilizes a very low bandwidth and can persist for an extended period of time. That makes it hard to detect and mitigate and can cause significant damage. It has proven to be highly effective against various types of web server software, such as Apache 1.x and 2.x.
History and Evolution of the Slowloris Attack
The Slowloris attack made its debut in 2009 when security researcher Robert “RSnake” Hansen developed it as a proof of concept to demonstrate a critical vulnerability in how web servers handle HTTP connections. The attack was designed to be a “low-and-slow” method of disabling servers, relying on minimal bandwidth compared to traditional Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. An interesting fact is that the attack gets its name from a type of slow-moving Asian primate that completes the job by moving slowly but steadily.
Initially, Slowloris proved devastating to older versions of Apache web servers, which struggled with handling numerous incomplete connections. Its low resource usage and stealthy nature made it a favored tool for ethical hackers and malicious attackers alike. Over time, the cybersecurity community responded by developing countermeasures, such as increasing connection timeouts, implementing rate limiting, and adopting web application firewalls.
As server technology evolved, the attack’s effectiveness was reduced against modern, more resilient systems. However, Slowloris remains a relevant threat for unpatched or legacy systems and highlights the ongoing need for robust server security.
Why Are Slowloris Attacks Dangerous?
Slowloris attacks are more difficult to detect because they send partial, instead of corrupted, packets. That is especially challenging when the attacker uses a group of infected devices to initiate a Slowloris DDoS attack. Therefore, traditional intrusion detection systems are less effective at detecting this type of DDoS attack. Furthermore, if a Slowloris attack goes unnoticed, it can persist for a prolonged period, causing significant harm.
Here are the main reasons why Slowloris attacks are so dangerous:
- Hidden: They are challenging to detect as they use low bandwidth and slowly consume server resources over time.
- Persistent: These attacks can last for an extended period, making them more difficult to mitigate than other types of DDoS attacks.
- Disruptive: Slowloris attacks can cause significant harm to a website or server by disrupting its performance and causing slowdowns, crashes, and data loss.
- Resource intensive: The attack demands large amounts of server resources to defend against it, potentially leading to decreased performance or complete failure of the target.
- Widespread impact: Slowloris attacks can impact not only the targeted website or server but also its users and customers, who may experience slowdowns, errors, or complete unavailability.
Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!
How does it work?
The Slowloris attack works by sending a massive amount of incomplete HTTP requests to the target web server. The cybercriminal sends partial requests, which never get fully established. The target server holds these connections open, waiting for the missing information. Over time, the increased number of open connections begins to consume the server’s resources, eventually becoming incapable of processing legitimate requests. This results in a Denial of Service (DoS) attack, causing the server to become slow, unresponsive, or even crash.
The Slowloris attack is performed mainly in the following four steps:
- Multiple Connections: The attacker opens multiple connections to the targeted server by sending multiple partial HTTP request headers.
- Server Threads: The target opens a thread for each incoming request, planning to close it once the connection is completed. Yet, if a connection takes too long, the server will time it out to free up the thread for new requests.
- Keeping Connections Alive: To stop the target from timing out the connections, the attacker periodically sends partial request headers to maintain the request alive. Basically, it says, “I’m still here! I’m just slow. Please wait for me!”
- Resource Exhaustion: The targeted server cannot release any open partial connections while waiting for the termination of the request. Once all available threads are in use, the server will be unable to respond to requests from regular traffic, leading to a Denial of Service (DoS).
The main advantage of the Slowloris attack is its ability to cause significant damage with very little bandwidth consumption.
What are the signs of Slowloris attack?
A Slowloris attack, as its name indicates, is slow and methodical in its approach. The attack sends partial HTTP requests to the targeted web server yet never completes them. As a result, the server opens more and more connections in expectation of the requests being completed.
Over time, the server’s maximum number of connections is gradually occupied, leaving no room for legitimate requests to be processed. For high-traffic websites, it may take longer for Slowloris to take control fully, but eventually, the attack will block all valid requests.
Here are some of the signs of an appearing Slowloris attack:
- Slow website performance – Your website may suddenly become slow or unresponsive.
- High server resource usage – If you notice a sudden increase in server resource usage, such as high CPU or memory usage, it could indicate a Slowloris attack.
- Error messages – If you receive error messages, such as “504 Gateway Timeout” or “403 Forbidden,” it could be a sign that your website is under attack.
- Increased traffic – If you witness an unexpected spike in traffic, it could signify that a Slowloris attack is targeting your website.
- Connection reset messages – If you receive connection reset messages, it may indicate that the attacker is attempting to disrupt your website’s connections.
It’s crucial to monitor your website and server performance closely and take action if you suspect that you are under attack. Early detection and response are essential to mitigating the effect of a Slowloris attack.
How to protect yourself?
Implementing different techniques for protection and mitigation is crucial for keeping your website or service safe from these attacks. Here are some things you could do in order to avoid Slowloris attacks:
- Increase web server connection limits: By increasing the maximum number of open connections, you could reduce the vulnerability to Slowloris attacks. The attacker would have to increase the number of connections as well before they can overload the server.
- Implement rate limiting: You can restrict access based on particular usage factors in order to prevent a Slowloris attack. Some useful techniques are: limiting the number of connections one IP address is permitted to make, limiting the period a user is allowed to stay connected, and restricting slow transfer speeds.
- Use load balancers: Load balancing techniques can help buffer connections and implement multiple connection management techniques. That helps stop incomplete HTTP requests from impacting applications and web servers.
- Web application firewalls (WAFs): WAFs are helpful in defending against application attacks, like Slowloris. They recognize and block malicious traffic before it gets to your network.
- Implement DDoS protection: A DDoS protection service is highly recommended for providing an extra layer of security. It can help stop malicious traffic toward your website and guarantee that it will remain available to legitimate users.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Constant monitoring can be extremely beneficial for identifying different types of cyber-attacks early. That allows you to take action before the attack becomes too severe.
- Patch Systems: Keep your software and all systems up-to-date by regularly installing the latest security patches. That will help you stop attackers from exploiting known vulnerabilities.
- Upgrade Web Server Software: It is important to frequently upgrade the web server software. That way, it helps to address known security vulnerabilities that potential attackers can exploit.
Is there a difference between HTTP flood attack and Slowloris attack?
HTTP Flood Attack:
- Mechanism: This attack involves overwhelming a web server with a large number of HTTP requests. The attacker sends a flood of standard, legitimate requests in such a volume that the server cannot handle the load. This exhausts the server’s resources, making the website or web service unavailable to legitimate users.
- Target: The attack targets the server’s ability to process and respond to incoming HTTP requests.
- Intensity and Speed: HTTP flood attacks are typically high-volume and fast-paced. They aim to exhaust the server’s resources quickly.
Slowloris Attack:
- Mechanism: Slowloris is a more subtle and insidious form of DoS attack. Instead of overwhelming the server with a flood of requests, it sends partial HTTP requests and keeps these connections open as long as possible by sending partial headers or periodically sending more headers, but never completing the request. The server, waiting for the completion of these requests, keeps each connection open. This gradually fills up the server’s connection table.
- Target: The attack specifically targets the server’s connection table, exploiting the fact that web servers can only handle a limited number of simultaneous connections.
- Intensity and Speed: Slowloris attacks are low-and-slow attacks. They do not require a large volume of traffic, making them more difficult to detect.
In summary, while both HTTP Flood and Slowloris attacks aim to make web services unavailable, they differ significantly in their method of execution: HTTP Flood overwhelms with a volume of complete requests, whereas Slowloris incapacitates by maintaining incomplete, long-lasting connections.
Slowloris vs. SYN Flood vs. Ping of Death
In the realm of cybersecurity, understanding the nuances of different attack methods is crucial. Slowloris, with its unique approach, stands in contrast to other common Denial of Service (DoS) techniques. Here’s a simplified yet insightful comparison:
Slowloris
- Modus Operandi: Slowloris quietly sends incomplete HTTP requests to a server, holding connection threads open indefinitely.
- Bandwidth Usage: Remarkably low, making it a stealthy, under-the-radar attack method.
- Detection Difficulty: Harder to detect due to its subtle nature, mimicking legitimate traffic.
- Target Vulnerability: Particularly effective against web servers with limited concurrent connection capabilities, like older versions of Apache.
SYN Flood
- Modus Operandi: In a SYN Flood, the attacker sends a rapid succession of SYN requests (part of the TCP handshake process) to a server, but never completes the handshake.
- Bandwidth Usage: Higher than Slowloris, as it involves sending numerous requests in a short period.
- Detection Difficulty: Easier to detect due to the unusual surge in incomplete connections.
- Target Vulnerability: Affects servers by overwhelming their ability to handle new connections.
Ping of Death
- Modus Operandi: PoD attack involves sending malformed or oversized packets using the ICMP protocol, which can crash or destabilize a server.
- Bandwidth Usage: Can vary, but generally noticeable due to the abnormal packet size.
- Detection Difficulty: Relatively easier to spot because of the packet anomalies.
- Target Vulnerability: Effective against systems that fail to handle irregular packet sizes properly.
To sum up, while Slowloris opts for a stealthy, low-bandwidth approach, other methods like SYN Floods and Ping of Death are more about overwhelming force. Knowing these differences helps in tailoring defenses against these varied cyber threats.
Real-Life Examples of Slowloris Attacks
Slowloris attacks have played a role in several high-profile incidents, showcasing their disruptive potential when targeting vulnerable systems.
In 2009, during a period of political tension, Iran accused the United States of employing Slowloris attacks against its government websites. These prolonged attacks, lasting several weeks, caused severe disruption to key online services, preventing communication and access to key resources.
In 2011, the hacker group LulzSec allegedly used a Slowloris attack to target the CIA’s public website. Although no classified systems were compromised, the attack made the site inaccessible for several hours. This incident draws attention to the vulnerability of even high-profile organizations to such low-bandwidth, high-impact tactics.
More recently, in 2018, a group of hackers known as MoneyTaker reportedly launched a coordinated Slowloris attack against several Russian banks. The attack temporarily turned off their websites, making them inaccessible to customers and causing reputational damage. This incident emphasized the potential financial and operational fallout of the Slowloris attacks when used against the banking sector.
Conclusion
The Slowloris attack is a dangerous Denial of Service (DoS) attack that sends many incomplete HTTP requests to a targeted server, leading to slowdowns, crashes, and data loss. This attack is difficult to detect and can persist for a prolonged period, making it highly effective and disruptive. That is why it is important to monitor your website’s performance and resource usage, be aware of the signs of an attack, and implement protective measures, such as firewalls and DDoS protection services. By doing so, you can keep your online presence secure and running smoothly.




