Why does the battle between TCP monitoring vs UDP monitoring matter in the world of network management? In this guide, we’ll delve into the heart of digital communications, revealing how these two monitoring strategies shape our online experiences. From ensuring seamless streaming to securing sensitive transactions, understanding the nuances of TCP and UDP can unlock new levels of performance and reliability. Are you prepared to dive deeper and discover how these protocols can transform your network’s efficiency? Join us as we explore the critical distinctions and advantages of TCP and UDP monitoring, paving the way for a smoother, more secure internet.
Table of Contents
Introduction to TCP and UDP
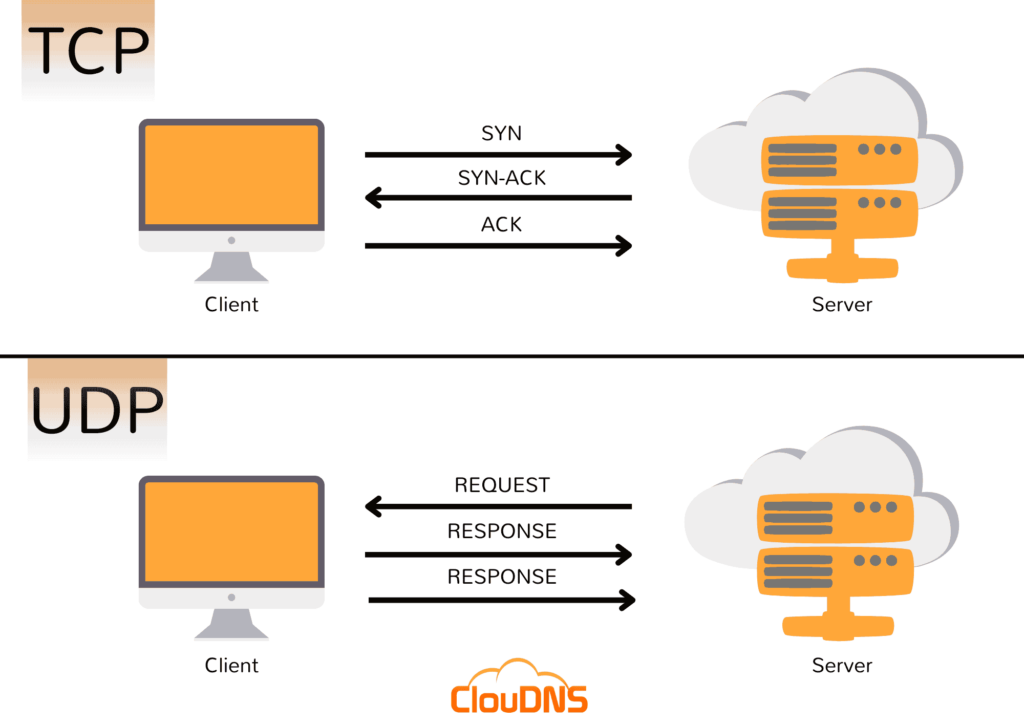
In the digital communication world, two primary protocols govern data transmission over the internet: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). TCP is renowned for its reliability, establishing a connection before data transfer to ensure all packets are received correctly and in order. This makes it ideal for applications where data integrity is paramount, such as web browsing, email, and secure transactions. On the other hand, UDP offers a connectionless communication model, prioritizing speed and efficiency over reliability. This makes it suitable for applications where fast data transmission is crucial, even at the risk of occasional data loss, such as streaming services, online gaming, and VoIP calls.
Understanding TCP Monitoring
TCP monitoring is a method to ensure that services requiring reliable data transmission are always available and performing optimally. It serves as a diagnostic tool to identify issues in network communication and application performance.
How It Works
TCP monitoring involves scrutinizing the state of TCP connections and the performance of applications using TCP. It includes checking whether a TCP connection can be successfully established on a specified port and monitoring the data transfer’s reliability and efficiency.
Benefits
- Reliability Assurance: Guarantees that applications dependent on TCP are consistently available and data integrity is maintained.
- Performance Optimization: Helps in identifying bottlenecks and improving the speed and efficiency of data transmission.
- Issue Detection and Resolution: Facilitates early detection of network problems, allowing for timely troubleshooting and minimization of downtime.
UDP Monitoring: An Overview
UDP monitoring is a technique used to ensure that applications which do not require reliable data transmission but need high speed and efficiency are running correctly.
How It Works
UDP monitoring checks the availability of services using the UDP protocol by sending packets to a specified port and waiting for a response. Unlike TCP, it does not establish a connection, making the monitoring process less intrusive and faster.
Benefits
- Speed Verification: Confirms that services are performing at the required speed for optimal user experience.
- Service Availability: Ensures that UDP-based services are accessible to users when needed.
- Efficiency Improvement: Helps in detecting inefficiencies and potential disruptions in real-time services.
Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!
TCP Monitoring vs UDP Monitoring
While both TCP and UDP monitoring are vital for network health, their applications and focus areas differ significantly:
- Application Sensitivity: TCP monitoring is essential for applications that cannot tolerate data loss, such as web and email services. UDP monitoring, however, is crucial for applications where speed and efficiency are more critical than absolute reliability, such as live video streaming or online gaming.
- Monitoring Focus: TCP monitoring emphasizes connection reliability and order of data delivery, while UDP monitoring targets service availability and performance metrics for applications sensitive to delays.
- Security Considerations: Both protocols require monitoring for security, but the nature of the threats may differ. TCP monitoring often looks for signs of connection hijacking or data tampering, whereas UDP monitoring might focus more on flood attacks or packet spoofing.
| Feature | TCP Monitoring | UDP Monitoring |
| Protocol Type | Connection-oriented | Connectionless |
| Reliability | High (guarantees delivery) | Low (does not guarantee delivery) |
| Data Flow Control | Yes (manages packet flow to prevent congestion) | No (sends data without flow control) |
| Error Correction | Yes (automatic retransmission of lost packets) | No (applications must handle errors) |
| Use Cases | Web browsing, email, file transfers | Streaming, online gaming, VoIP |
| Monitoring Focus | Connection stability, packet sequence, error detection | Packet loss, jitter, application performance |
| Benefits | Ensures data integrity and order | Optimizes speed and efficiency for real-time applications |
How to Manually Monitor TCP/UDP Ports
Monitoring TCP and UDP ports is a fundamental task in network management and security. While manual methods using command-line tools are effective, they require entering specific commands and interpreting results to gain insights into port activity.
On Windows
- Netstat: A built-in tool for viewing active connections and listening ports. To use it:
- Run netstat -an in Command Prompt to display a list of open ports and their statuses.
- TCPView: A graphical utility from Microsoft Sysinternals. It offers a user-friendly interface to view TCP and UDP endpoints, showing the owning process name and ID.
On Linux/UNIX
- Netstat: Displays open ports and active connections. Use netstat -tuln to list TCP and UDP listening ports.
- SS: A modern alternative to netstat, ss provides detailed connection information. The command ss -tuln displays open TCP/UDP ports.
- LSOF: The lsof (List Open Files) command identifies listening ports. Running lsof -i reveals the ports used by active processes.
Manual monitoring is effective for basic tasks and troubleshooting, but automated tools offer enhanced convenience, scalability, and advanced features. They are ideal for ongoing network management and maintaining robust security.
The Role of Firewall Monitoring
Within the intricate web of network security practices lies the critical and engaging process known as firewall monitoring. This method meticulously assesses the operational status and effectiveness of firewall configurations, employing TCP and UDP monitoring checks to ensure that specific ports on devices align perfectly with the intended firewall rules and policies.
For example, by deploying a TCP monitoring check to validate the accessibility of port 443, essential for HTTPS traffic, administrators can swiftly be alerted to the service’s status – UP if the port is securely open, confirming that encrypted web services are operational and secure, or DOWN if the port is unexpectedly closed or unresponsive, indicating a critical issue that could compromise secure web access and data integrity.
Suggest page: What HTTP/HTTPS Monitoring is?
This method allows for precise control and verification of firewall functionality, ensuring that only authorized traffic can access the network, thereby significantly enhancing the security posture against potential intrusions or data breaches.
Conclusion
Monitoring TCP and UDP traffic is essential for maintaining network performance, reliability, and security. While TCP monitoring focuses on ensuring data integrity and smooth flow, UDP monitoring is critical for optimizing real-time application performance. Together with firewall monitoring, these practices provide a comprehensive approach to network management, safeguarding against disruptions and threats while ensuring a seamless user experience. As networks evolve, adopting sophisticated monitoring tools and techniques will remain integral to achieving operational excellence and security resilience.