Everybody uses CDN (Content Delivery Network). YouTube, Amazon, Netflix and many others are applying it on a massive world scale so you can enjoy your favorite content in a matter of milliseconds. But how does it work?
Table of Contents
What is CDN?
CDN (Content Delivery Network) is a network of geographically distributed servers all around the world. Each of these servers is a PoP (Point of Presence). It has a cache of the data that the users in this specific location will use. CDN doesn’t substitute the web hosting; it just makes many cached data of the original data and stores it around the world for better accessibility. It works using the GeoDNS technology so the visitors of your website will be connected to the fastest/closest server, without the need to get the data from the web hosting. CDN saves a lot of time.
Why is it important?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is important because it improves the performance, scalability, and security of websites and applications. By distributing content across multiple servers located in different geographic locations, CDNs can deliver content faster and more efficiently to users. That way, it reduces latency, improves page load times, and provides a better user experience. CDNs can also handle high volumes of traffic, reducing server load and improving website scalability. Furthermore, CDNs offer security features such as DDoS protection and web application firewalls, which help protect against cyber threats. Overall, CDNs are an essential tool for modern businesses that rely on fast and efficient content delivery, global reach, and robust security.
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
History of CDN
Different technologies affected the birth of CDN – hierarchical caching, server farms, cache proxy deployment and improved web servers.
The first generation of CDN came around the late 90’s. People created them because of the growing use of on-demand content (audio, video, etc.). Dynamic and static content delivery. It was mostly intelligent routing and edge computer methods. The second and current generation, is cloud-based, relying on a peer-to-peer connection and it is focused on video-on-demand.
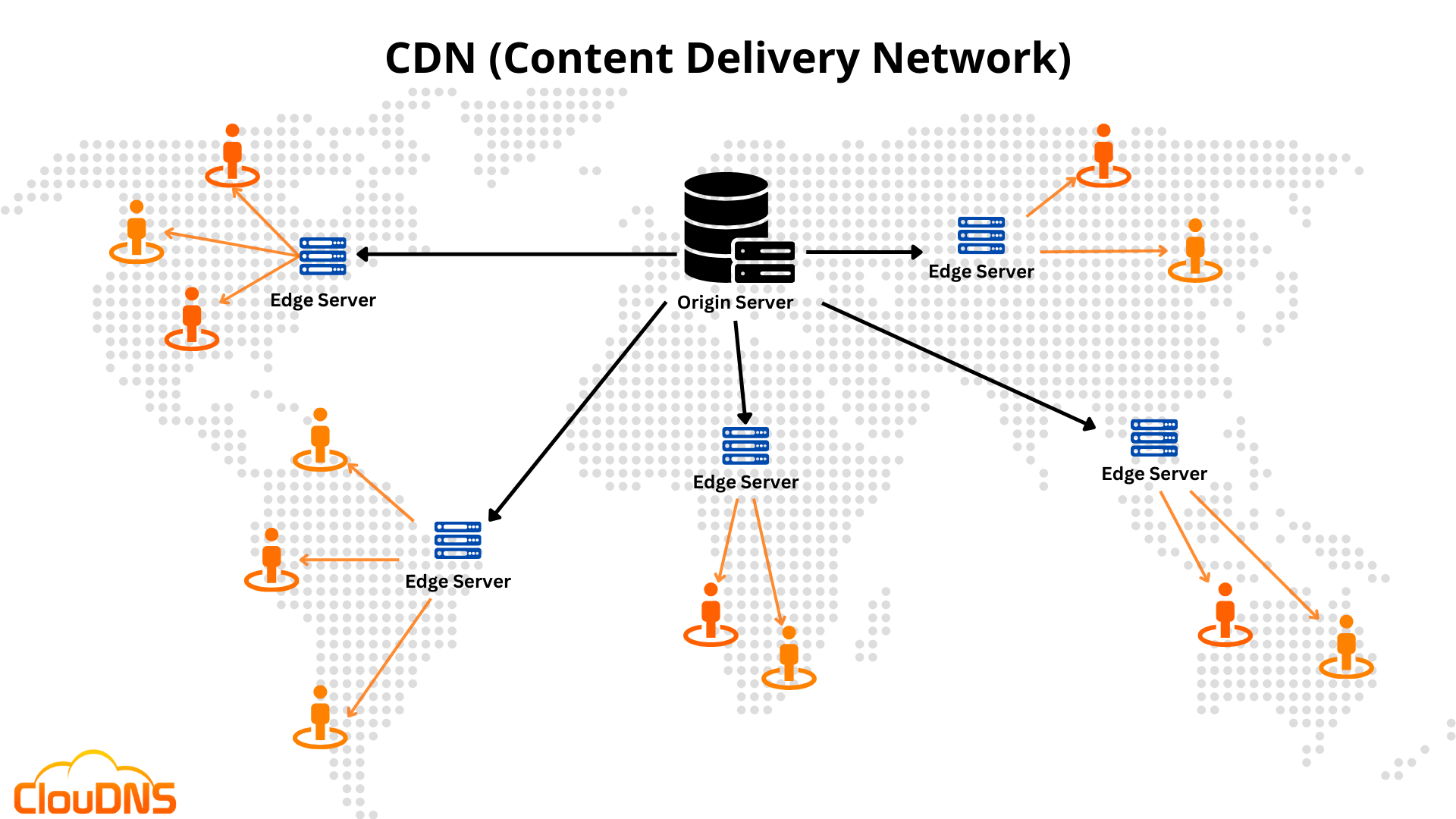
How does it work?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a system of servers distributed geographically to deliver web content to users more quickly and efficiently. When a user requests a web page, the CDN provides the content from a server closer to the user’s location, reducing the time it takes to load.
The process of delivering content through a CDN typically involves the following steps:
- A user requests a website or a specific web page from their browser.
- The user’s request is received by the nearest CDN server, called an edge server, to their geographic location. The edge server is determined based on the user’s IP address, which reveals their location.
- If the edge server has a cached copy of the requested content, it serves it directly to the user’s browser. Caching involves storing a copy of the content on the edge server. That way, it can be delivered more quickly to users in the future.
- If the edge server doesn’t have a cached copy of the content, it requests it from the origin server. The origin server is the original source of the content, typically the website’s hosting server.
- The origin server responds by sending the requested content to the edge server.
- The edge server caches the received content from the origin server for future requests.
- Finally, the edge server provides the requested content to the user’s browser.
By distributing content across multiple servers, a CDN can reduce the load on the origin server and provide a more reliable and scalable infrastructure for delivering content to users worldwide. Additionally, since edge servers are located closer to users, the time it takes to load web pages is significantly reduced, improving the user experience.
For who is it?
Anyone can benefit from CDN. From the big companies that we mentioned before and small blog websites. The technology increases the speed of the website and can be very useful even if you have just a WordPress blog. This helps the SEO, and your website will rank a lot better in Google, and your visitors will be happier thanks to the speed boost.
Here are some examples of who can benefit the most from implementing a CDN:
- E-commerce Platforms: E-commerce websites can experience irregular traffic patterns, especially during peak shopping seasons or promotional events. CDNs help these platforms deliver product images, videos, and web pages quickly and efficiently to customers worldwide, ensuring a seamless shopping experience and maximizing sales.
- Media and Entertainment Companies: Streaming services, gaming platforms, and content providers rely heavily on CDNs to deliver high-quality audio and video content to users across different locations, devices and platforms. CDNs minimize buffering, reduce latency, and ensure smooth playback, enhancing the overall user experience and driving engagement.
- Software Companies: Software companies distribute updates, patches, and installation files to users globally. CDNs accelerate the download process, reduce bandwidth consumption, and ensure reliable delivery of software updates, enabling users to access the latest releases quickly and securely.
- News and Publishing Websites: News websites and publishing platforms require fast and reliable content delivery to keep readers informed and engaged. CDNs ensure timely delivery of articles, images, and multimedia content, even during periods of high traffic volume or breaking news events, enhancing reader satisfaction and retention.
- Gaming Industry: Online gaming platforms depend on low-latency, high-performance networks to deliver an immersive gaming experience to players worldwide. CDNs minimize lag, reduce packet loss, and optimize server response times, providing gamers with enhanced gameplay experiences.
How to create your CDN using DNS
Types of Content Delivered by CDNs
Content Delivery Networks are versatile systems that efficiently deliver various types of content to users worldwide. Here are some of the primary types of content delivered by CDNs:
Static Content:
CDNs excel at delivering static assets such as images, CSS stylesheets, JavaScript files, HTML, and downloadable files (like PDFs or software). These files do not change based on user interactions and can be cached effectively at edge servers, ensuring fast and reliable delivery.
Dynamic Content:
While traditionally challenging to cache, CDNs now leverage advanced technologies to optimize the delivery of dynamic content, such as web pages or data that change based on user actions, such as personalized dashboards or shopping carts. By reducing server load and employing intelligent routing, CDNs minimize latency for dynamic elements.
Streaming Media:
CDNs play a pivotal role in delivering high-quality streaming media, including live and on-demand video and audio. By reducing latency and buffering, they provide a seamless viewing and listening experience for users.
APIs and Software Updates:
CDNs distribute API responses and deliver software updates, patches, and installation files efficiently, ensuring minimal downtime and high reliability.
By efficiently handling diverse content types, CDNs enhance user experiences, reduce latency, and improve overall website performance.
Benefits
CDN is able to provide numerous benefits, some of which are the following:
- The most significant benefit is definitely the speed. It reduces the latency; everything loads way faster than before. How fast? On average 70% faster!
- Load balancing. By using different PoPs around the world, the traffic gets well distributed, and it reduces the traffic on the original server.
- It reduces the bandwidth consumption, so if your web host has low bandwidth, this can help you a lot.
- It has DDoS protection. It protects you from a single point of failure, thanks to the many different PoPs.
- It will improve the SEO of your site. Google values the speed of your website as one of the key indicators for ranking in its search engine.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks are getting more popular thanks to its advantages. Many people start using it for E-commerce Entertainment and blog sites. It can help you over rank your competitors on the Google pages and provide a better uptime. There is no doubt that this solution is definitely worth trying!