We have already talked about what is DNS and what is a Secondary DNS, this time we will focus on the Primary DNS server. There is a DNS hierarchy in which the Primary is taking the central spot. It has the latest and full information, in comparison with lower level DNS servers who have just a cache of this information and with an expiry period. So, let’s explain a little bit more about the Primary DNS server and how it works!
Table of Contents
Primary DNS server explained
The Primary DNS server is also known as Master server. It is responsible for hosting the zone file. This file contains information about the domain in forms of DNS records. Each domain can have just one Primary DNS server. You can manage the zone by those DNS records. You can add, edit or delete those records. The Primary also synchronizes its data with the rest of the servers if there are some. There are usually Secondary DNS servers who have a copy of the zone data. This helps with redundancy and guarantees more up time.
How does the Primary DNS server work?
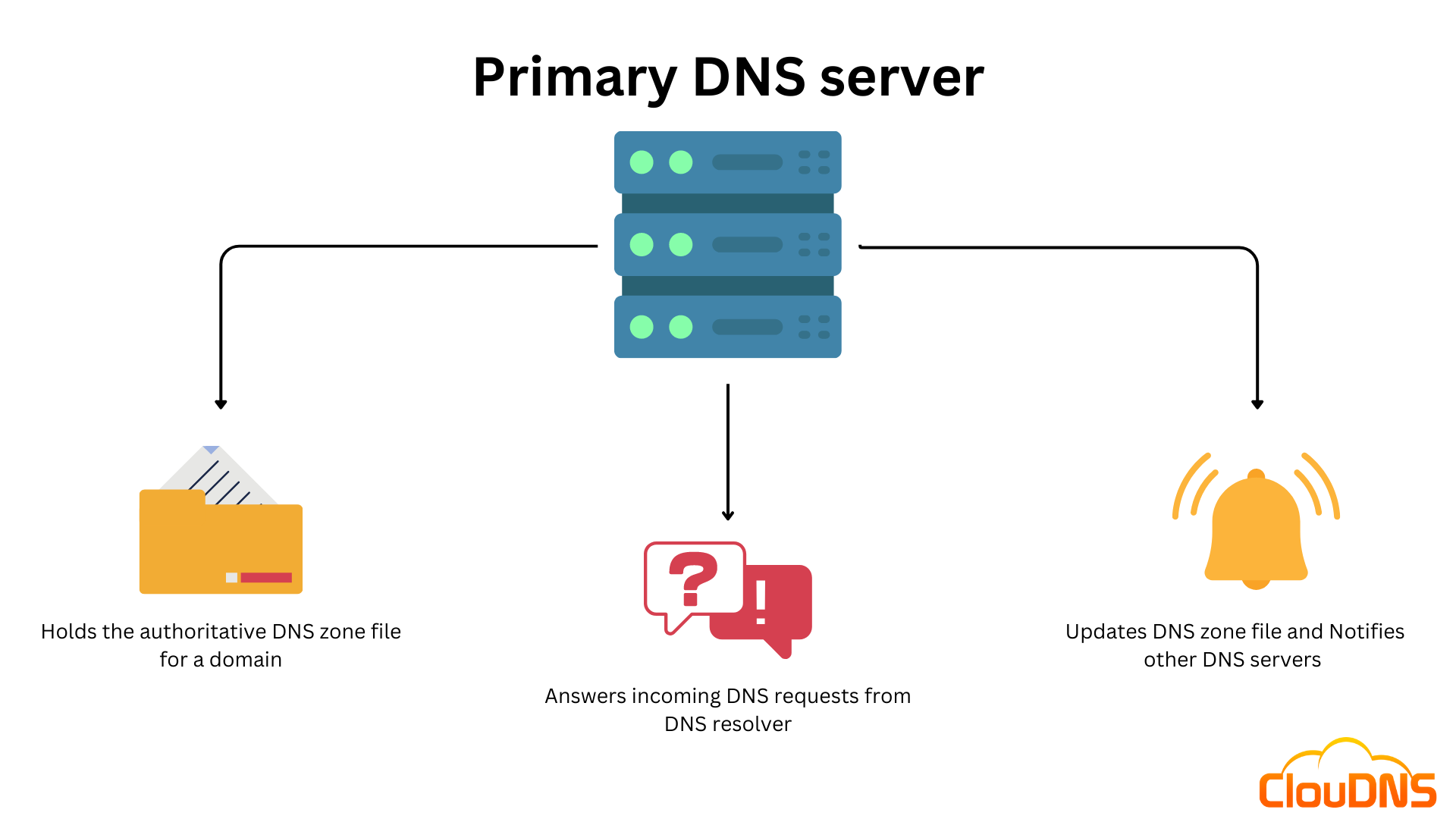
The Primary DNS server is responsible for maintaining the authoritative copy of the DNS zone file for a particular domain. The DNS zone file contains information about the domain’s resource records, such as IP addresses, MX records, and NS records.
When a recursive server receives a DNS query for a domain, it will search for the IP address associated with that domain. If the DNS resolver is configured to use the Primary DNS server for the domain, it will send the DNS query to that server. The Primary will then search its zone file to find the requested information and send it back to the DNS resolver, which will, in turn, return the information to the user.
The Primary is also responsible for updating the DNS zone file with any changes that occur to the DNS data. These changes can happen, for example, when creating a new DNS record or adding a new email server. Once the Primary DNS server updates the zone file, it notifies other DNS servers that it is authoritative for that domain, so they can update their own cache accordingly.
Is just a single Primary DNS server enough?
Yes, it is possible for a single Primary DNS server to be sufficient for a domain name, yet it poses a significant risk of a single point of failure. If the server experiences any issues such as maintenance, updates, power outages, or technical difficulties, there will be no backup to respond to DNS queries. Therefore, it is recommended to have a network of at least a few Secondary DNS servers that can share the load, reducing stress on the Primary DNS server and providing redundancy.
How to protect your Primary DNS?
There are different approaches for keeping your Primary DNS safe and protected.
First let’s think about the data flow. In every step, where there is a data transfer, there could be a potential threat.
- The zone file. It can get corrupted by an accidental mistake or malicious activities. It should be secure, and you need to do a backup often. Also you will need an excellent administrator to handle it.
- Dynamic updates. Here, significant threats are the unauthorized updates. You can limit only specific IP to be able to make such updates.
- Zone transferring. Again, limit the IPs which can do it.
- Remote queries. Better use a secure VPN for this kind of interaction or someone can intercept your remote queries.
The second excellent solution for guaranteeing the security and protection of your network is Secondary DNS. Once you implement it, you will have an additional set of Authoritative DNS servers for your domain name. That way, if your Primary DNS server fails and is not able to handle the incoming DNS requests for your domain, the Secondary DNS servers will handle the load, and your website or service will remain available for your clients. Secondary DNS is also known as Backup DNS due to the fact it makes a copy and stores all of the DNS data (DNS records) for your domain. So, it is a secure backup if you lose your original information.
How to use both Primary DNS and Secondary DNS?
You can use ClouDNS as your Primary DNS provider and use another company for Secondary DNS or vice versa. Just remember that you control the zone file through your Primary DNS, so better choose a provider that offers easy to use control panel and has excellent customer service.
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
How to choose the right Primary DNS Server provider?
Selecting the right Primary DNS server provider is crucial for ensuring reliability, performance, and security for your domain. Here are key factors to consider:
- Performance and Uptime: Look for a provider with a proven track record of high uptime (ideally 99.99% or more) and fast DNS query resolution speeds. Downtime or slow responses can negatively impact your website’s availability and user experience.
- Scalability: Choose a provider that can scale with your needs. Whether your domain serves a small website or a global enterprise, the provider should handle growing traffic and query demands without sacrificing performance.
- Security Features: Choose a provider that offers robust security measures like DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions), DDoS protection, and advanced access controls to prevent unauthorized changes or attacks on your DNS records.
- User-Friendly Management: A provider with an intuitive control panel or API simplifies DNS record management. This is especially important if you need to make frequent updates or manage multiple domains.
- Support and SLA: Ensure the provider offers 24/7 customer support and a solid Service Level Agreement (SLA) guaranteeing performance standards.
Why is the Primary DNS Server important?
The Primary DNS server is fundamental in the Domain Name System (DNS) hierarchy, serving as the authoritative source for a domain’s DNS zone file. It is responsible for storing and managing all critical DNS records, such as IP addresses (A and AAAA records), mail server details (MX records), and name server entries. This central role ensures accurate and consistent resolution of domain names to their corresponding IP addresses, enabling seamless access to websites, email, and other online services.
Without a reliable Primary DNS server, any changes to the DNS zone file cannot be propagated to Secondary DNS servers, potentially leading to outdated or incorrect information being delivered to users. Additionally, the Primary DNS plays a vital role in DNS updates, ensuring new records or modifications are properly handled. Its importance extends to network reliability, as a well-maintained Primary DNS server minimizes downtime and improves user experience across the internet.
Best Practices for Primary DNS Server Management
Let’s talk a little bit about the best practices when it comes to managing a Primary DNS server:
- Regular Backups: Performing regular backups of the Primary DNS Server’s configuration and zone files is essential. It safeguards against data loss. This practice ensures that, in the event of a server failure or other catastrophic events, administrators can quickly restore the DNS data to its previous state.
- Monitoring and Logging: Implementing comprehensive monitoring and logging tools helps administrators track the performance and health of the Primary DNS Server. Monitoring tools can provide insights into query volumes and response times and detect unusual or suspicious activities. The practice is crucial for identifying potential issues and mitigating security threats.
- Redundancy and High Availability: To enhance reliability, administrators should configure Secondary DNS servers to provide redundancy. Secondary servers will still respond to DNS queries if the Primary DNS server becomes unavailable, which also helps minimize downtime.
- Security Measures: The security of the Primary DNS Server is paramount to prevent unauthorized access or tampering. Implementing secure practices, such as access controls, firewalls, and routine security audits, helps safeguard the integrity of the DNS records.
- Regular Updates and Patching: Keeping the DNS server software up-to-date with the latest patches and updates is crucial for handling security vulnerabilities and ensuring optimal performance. Regular updates also help incorporate new features and improvements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Primary DNS server is a crucial component of the DNS hierarchy, responsible for maintaining the authoritative copy of the DNS zone file for a particular domain. It plays a central role in DNS resolution, and keeping it safe and protected is essential.
Hi, I’m Martin Pramatarov. I have two degrees, a Technician of Computer Networks and an MBA (Master of Business Administration). My passion is storytelling, but I can’t hide my nerdish side too. I never forgot my interest in the Hi-tech world. I have 10 years and thousands of articles written about DNS, cloud services, hosting, domain names, cryptocurrencies, hardware, software, AI, and everything in between. I have seen the Digital revolution, the Big migration to the cloud, and I am eager to write about all the exciting new tech trends in the following years. AI and Big Data are here already, and they will completely change the world!
I hope you enjoy my articles and the excellent services of ClouDNS!